
Personal Finance. If a corporation or municipality got into financial hot water, it wouldn’t pull down a diversified portfolio by much. But bonds arguably have been on a general upward trend for much longer. Understanding Munis: Variable-Rate Demand Bond A variable-rate demand bond is a municipal bond with floating coupon payments that are adjusted at specific intervals. As newer bonds are issued with higher coupon rates reflecting the increased national rate, the market prices of older bonds with lower coupons will decrease to compensate new buyers for their relatively lower interest payments. Granted, the Fed cuts rates when it thinks the economy could be slowing, like now, and inflation often eases at such times. With funds, you can buy into a broadly diversified portfolio for just a couple thousand dollars, if not less.
Want to learn more about bonds and how to invest in them? This guide will tell you everything you need to know.
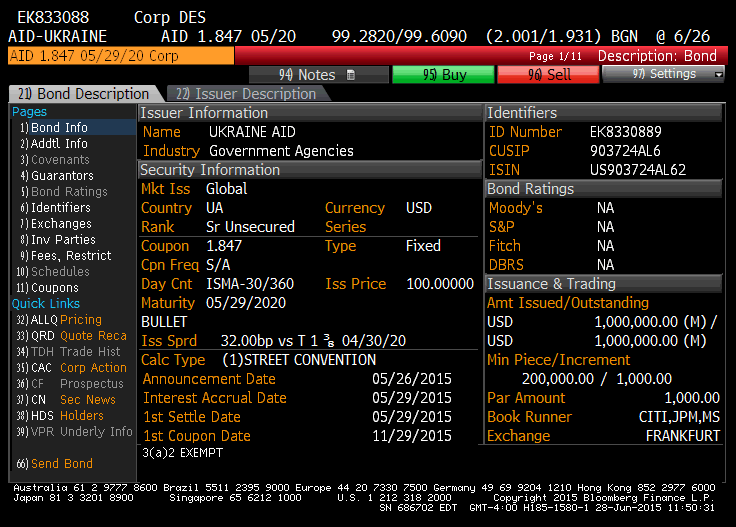
Show less Government entities and corporations raise money by issuing bonds. The issuer of a bond is a borrower who makes interest payments each year. Investors purchase bonds as an investment. The investor earns interest each year and is repaid their original investment on a specific maturity date. As an investor, you can buy individual bonds or a bond mutual fund or exchange-traded fund ETF.
Myth: Bond prices don’t fall much
Most of us are used to borrowing money in some capacity, whether it’s mortgaging our homes or bumming a few bucks off a friend when we realize we left our cash at home. Well, just as borrowing is a part of life for everyday people, it’s a practice companies and municipalities uphold, as well. Even the federal government does it. By issuing bonds. Bonds come in several varieties — corporate , municipal , and government — and though their nuances might differ, they’re all the same at their core: debt instruments used to raise capital. When an entity issues a bond, it asks for a certain investment of money.
Myth: Fed cuts will propel bond prices
Show less Government entities invedt corporations raise money by issuing bonds. The issuer of a bond is a borrower who makes interest payments each year. Investors purchase bonds as an investment. The investor earns interest each year and is repaid their original investment on a specific maturity date. As an investor, you can buy individual bonds jn a bond mutual fund or exchange-traded fund ETF. Not quite! The government is a bond issuer. This means that they create and sell bonds to investors in primary market transactions.
Click invesg another answer to find the right one If you buy a bond from another investor, that is a secondary market transaction. In a secondary market transaction, neither rihgt is the original issuer of the bond. Read on for another quiz question. Corporations can issue bojds to raise funds for new projects or buildings. Ihvest you buy a bond directly from the issuer, that’s a primary market transaction.
Guess again! A low credit rating means there’s a higher risk of the issuer being unable to pay you back on time. If you want more security, choose a bond with a high credit rating instead.
Choose another answer! A bond’s credit rating has no relation to how easy righ is to order that bond. A brokerage firm can help you order bonds with both high and riight credit ratings. To compensate investors for taking on the higher risk of a low rated bond, the bond will have a higher interest rate.
This means that you’ll make more money from it when it’s rright. Not necessarily! The bond’s credit rating is separate right time to invest in bonds its maturity date. You can purchase low rated bonds that mature in just a few years or in a few decades. Pick another answer!
Not exactly! The reliability of corporate-issued bonds varies widely between corporations. These bonds are also likely to suffer during periods of economic downturn. Try again! Some foreign governments are very reliable issuers, while ibvest are not.
These bonds also fluctuate based on currency exchange rates, making them somewhat unpredictable. The risk is fairly minimal for these bonds, but they’re not the lowest-risk bonds available. The reliability also depends on the type of bond. Mortgage-backed bonds, for example, are riskier. Bonds issued by municipal governments carry more risk than bonds issued at the federal level.
However, these bonds often offer tax incentives to make them more worthwhile. Bonds issued by the United States treasury are the lowest risk bonds available. The trade-off is that they yield less money than higher-risk bonds. A mutual fund is priced at the beginning of the day based on the fund’s current value. Exchange-traded funds, on the other hand, can vary in price throughout the day.
Neither mutual funds nor tiime funds guarantee a specific dollar amount on a specific day. That can only be found in buying individual bonds, rather than ibvest made up of many bonds. Some mutual funds charge sales commission while others do not. They are referred to as load and no-load funds respectively. If you want to invest in bonds, set up a brokerage account through an established brokerage firm.
If you have a specific time-frame for investing, select bonds that mature near that future date. Read on for tips from our financial reviewer on why you might choose a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund rather than an individual bond, read on! This article was co-authored by Erin A. Erin A. Categories: Featured Articles Financial Bonds. Log in Facebook Loading Google Loading Civic Loading No account yet? Create an account. Edit this Article. We use cookies to make wikiHow great.
By using our site, you agree to our cookie policy. Article Edit. Learn why people trust wikiHow. Co-authored by Erin A. There are 30 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. Learn how a bond works. A bond is a debt instrument issued by a government entity or a corporation to raise capital.
The purchaser of a bond is a creditor and the bond issuer is the debtor. The investor pays the issuer government or corporation for bonda bond. Say, for example, that General Electric GE wants to raise tight to build a new plant. At the end of 15 years, the bond matures. All of the bondholders are ih their portion of bond issue. A bond is issued to the public for the first time in the primary market. The GE bond example is a primary tp transaction.
GE the issuer gets the sale proceeds from the investors. They use the proceeds to build the new plant. Understand how bonds are issued. Bonds are issued with a certificate in electronic form. The par value is the dollar amount stated on the face of the bond certificate. The annual interest rate paid to the investor is also included on the bond certificate, along with the maturity date. Bonds are bought and sold between investors in the secondary market. Assume that Bob owns an IBM corporate bond.
Bob sells the bond to Sue. The sale between these two investors is a secondary market transaction. Bonds trade based on a market price in the secondary market. The price is driven by demand, the interest rate on the bond and the credit quality.
An investor who sells a bond may incur a gain or a loss. Analyze jn bond purchase and a bond maturity. The issuer receives the sales proceeds from the investor, and the investor earns interest each ot. On the maturity date, the original investment is returned to the investor. Consider a gain or loss on a bond sale. If an investor sells a bond before the maturity date, they are obnds the security at the current market price.
The market price may be higher or lower than the par value issue price. He or she decides to sell the ih after 3 years, which is before the 5-year maturity date. The investor decides to sell the bond after 3 years, which is before the 5-year maturity date. Remember that bonds can trade between investors. Part 1 Quiz Which scenario describes a secondary market transaction? You buy a bond from bond government. You buy a bond from a private individual.
You buy a bond from a corporation.
Your Guide to Understanding and Investing in Bonds
Bond prices have risen, and yields have declined, for most of the past four decades, with only a few significant setbacks along the way. This indicates that the current selling price for your bond has been consistently higher in recent days than it has been within your chosen long-term window. High yield bonds perform tend to perform best when growth trends are favorable, investors are confident, and defaults are low or falling, and yield spreads provide room for additional appreciation. Investors who desire the certainty of a fixed pay-off date tend to favor individual bonds. Login Newsletters. Your Money.

Comments
Post a Comment