Certain complex options strategies carry additional risk. Informational Messaging. Real Estate Investing.
Why invest with Fidelity
An investment fund is a way of investing money alongside other investors in order to benefit from the inherent advantages of working as part of a group. These advantages include an ability to:. It remains unclear whether professional active investment fuhds can retieement enhance risk adjusted returns by an amount that exceeds fees and expenses of investment management. Terminology varies with country but investment funds are often referred to as investment poolscollective investment vehiclescollective investment schemesmanaged rteirementor simply funds. The regulatory term is undertaking for collective investment in transferable securitiesor short collective investment undertaking cf. An investment fund may be held by the public, such as a mutual fundexchange-traded fundspecial-purpose acquisition company or closed-end retirement funds investment company[1] or it may be sold only in a private placementsuch as a hedge fund or private equity fund. Investment funds are promoted with a wide range of investment aims either targeting specific geographic regions e.
Why invest with Fidelity

A RIF is generally a mutual fund that is well diversified in large and mid-cap stocks and bonds. A RIF balances its portfolio to allow for moderate gains using a conservative approach to attempt to retain value while providing income to investors. Retirement income funds are actively managed funds that are intended to provide conservative, moderate growth for assets tucked away for retirement purposes, such as IRAs. There is no special tax treatment for these funds despite their name; they are treated as normal mutual fund investments. As a mutual fund, they are exposed to market risk and are, therefore, not a guaranteed retirement income.
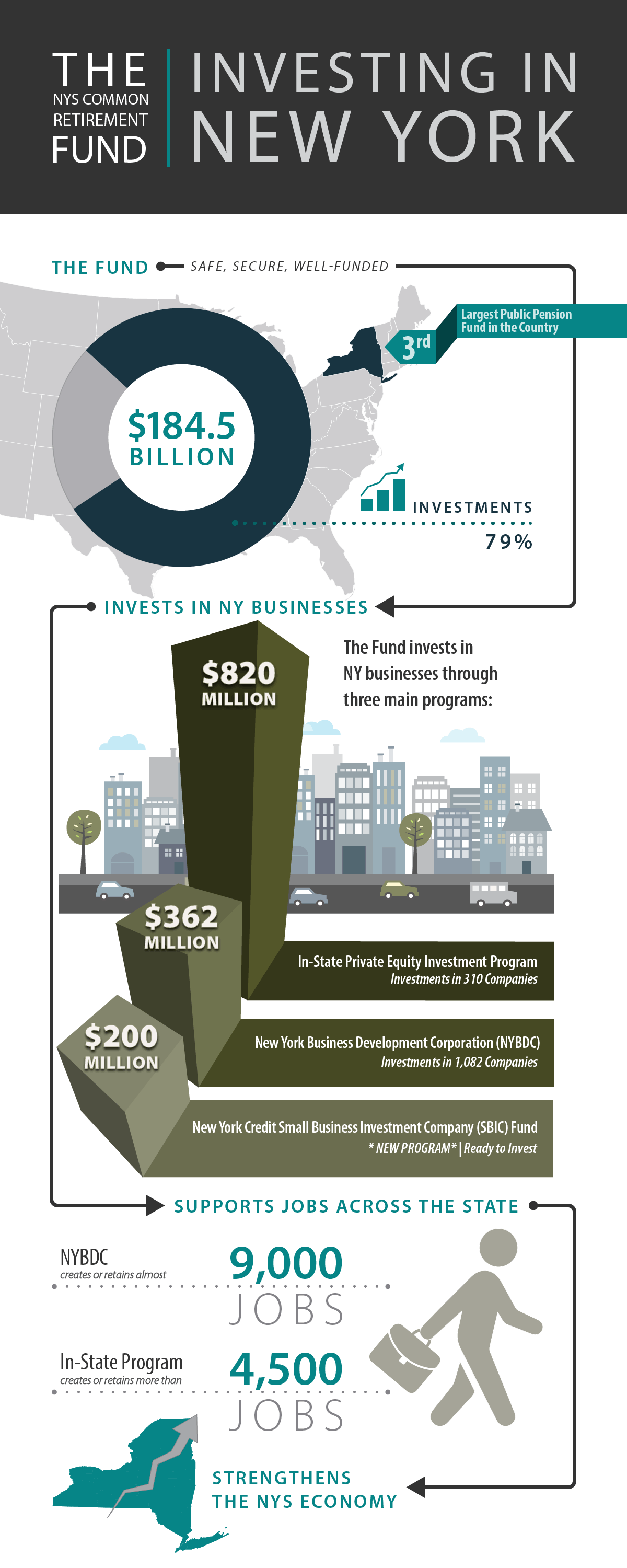
This Is Where Most Pension Funds Invest
An investment fund is a way of investing money alongside other investors in order to benefit from the inherent advantages of working as part of a inveetment. These advantages include an ability to:. It remains unclear whether professional active investment managers can reliably enhance risk adjusted returns by an amount that exceeds fees and expenses of investment management.
Terminology varies with country but investment funds are often referred to as investment poolscollective investment vehiclescollective investment fundssmanaged fundsor simply funds. The regulatory term is undertaking for collective investment in transferable securitiesor short collective investment undertaking cf. An investment fund may be held by the public, such as a mutual fundexchange-traded fundspecial-purpose acquisition company or closed-end fund[1] or it may be sold only in a private placementsuch as a hedge fund or private equity fund.
Investment funds are promoted with a wide range of investment aims either targeting specific geographic regions e. Depending on the country there is normally a bias towards the domestic market due to familiarity, and the lack of currency risk. Funds are often selected on the basis of these specified investment aims, their past investment performance, and other factors such as fees. The first recorded professionally managed investment funds or collective investment schemes, such as mutual fundswere established in the Dutch Republic.
The term «collective investment scheme» is a legal concept deriving initially from a set of European Union Directives to regulate mutual fund investment and management.
The basic aim of collective investment scheme regulation is that the financial «products» that are sold to the public are sufficiently transparent, with full disclosure about the nature of the terms.
In the United Kingdom, the primary statute is the Financial Retiremeny and Markets Actwhere Part XVII, sections to deal with the requirements for a collective investment scheme to operate. Collective investment vehicles may be formed under company lawby legal trust or by statute. The nature of the vehicle and its limitations are often linked to its constitutional nature and the associated tax rules for the type retirsment structure within a given jurisdiction.
Please see below for general information on specific forms of vehicles in different jurisdictions. The net asset value or NAV is the value of a vehicle’s assets minus the value of its liabilities. The method for calculating this varies between vehicle types and jurisdiction and can be subject to complex regulation.
An open-end fund is equitably divided into shares which vary in price in direct proportion to the variation in value of the fund’s net asset value. Each time money is invested, new shares or units are created to match the prevailing share price; each time shares are redeemed, the assets sold match the prevailing share price. In this way there is no supply or demand created for shares and they remain a direct reflection of the underlying assets. A closed-end fund issues a limited number of shares or units in an initial public offering or IPO or through private placement.
If shares are issued through an IPO, [ citation needed ] they are then traded on an exchange or directly through the fund manager to create a secondary market subject to market forces. If demand for the investjent is high, they may trade at a premium to net asset value. If demand is low they may trade at a discount to net asset value. Further share or unit offerings may be made by the vehicle if demand is high although this may affect the share price. For listed funds, the added element of market forces tends to amplify the performance of the fund increasing investment risk through increased volatility.
Some collective investment vehicles have the power to borrow money to make further investments; a process known as gearing or leverage.
If markets are growing rapidly this can allow the vehicle to take advantage of the growth to a greater extent than if only the subscribed contributions were invested. However this premise only works if the cost of the borrowing is less than the increased growth achieved.
If the borrowing costs are more than the growth achieved a net loss is achieved. This can greatly increase the investment risk of the fund by increased volatility and exposure to increased capital risk. Gearing was a major contributory factor in the collapse of the split capital investment trust debacle in the UK in Some vehicles are designed to have a limited term with enforced redemption of shares or units on a specified date.
Many collective investment vehicles split the fund into multiple classes of shares or units. The underlying assets of each class are effectively pooled for the purposes of investment management, but classes typically differ in the fees and expenses paid out of the fund’s assets.
These differences are supposed to reflect different costs involved in servicing investors in various classes; for example:. In some cases, by aggregating regular investments retiremet many individuals, a retirement plan such as a k plan may qualify to purchase «institutional» shares and gain the benefit of their typically lower expense ratios [ citation needed ] even though no members of the plan would qualify individually. These also include Unit Trusts. One of the main advantages of collective investment is the reduction in investment risk capital risk by diversification.
An investment in a single equity may do well, but investmeent may collapse for investment or other reasons e. If your money is invested in such a failed holding you could lose your capital. By investing in a range of equities or other securities the capital risk is reduced. Collective investments fudns their nature tend to invest in a range of individual securities. However, if the securities are all in a similar type of asset class or market sector then there is a systematic risk that all the shares could be affected by adverse market changes.
To avoid fnds systematic risk investment managers may diversify into different non-perfectly-correlated asset classes. For example, investors might hold their assets in equal parts funss equities and fixed income securities. If one investor had to buy a large number of direct investments, the amount this person would be able to invest in each holding is likely to be small. Dealing costs are normally based on the number and retirement funds investment company of each transaction, therefore the overall dealing costs would take a large chunk out of the capital affecting future profits.
The fund manager managing the investment decisions on behalf of the investors will of course expect remuneration. Retiremnt is often taken directly from the fund assets as a fixed percentage each year or sometimes a variable performance based fee. If the investor managed their own investments, this cost would be avoided. Often the cost of advice given by a stockbroker or financial adviser is built into the vehicle.
Often referred to as commission or load in the U. While this cost will diminish your returns it could be argued that it reflects a separate payment for an advice service rather than a detrimental feature of collective investment vehicles. Indeed, it is often possible to purchase units or shares directly from the providers without bearing rdtirement cost. Although the investor can choose the type of fund to invest in, they have no control over the choice of individual holdings that make up the fund.
If the investor holds shares directly, he has the right to attend the company’s annual general meeting and vote on important matters. Investors in a collective investment vehicle often have none of the rights connected with individual investments within the fund. Each fund has a defined investment goal to describe the remit of the investment manager and to help investors decide if the fund is right for. The investment aims will typically fall into the broad categories of Inveztment value investment or Growth investment.
Income or value based investment tends to select stocks with strong income investmen, often more established businesses. Growth investment selects stocks that tend to reinvest their income to generate rerirement. Each strategy has its critics and proponents; some prefer a blend approach using aspects of.
Funds are often distinguished by asset-based categories such as equitybondsproperty. Also, perhaps most commonly funds are divided by their geographic markets or themes. In most instances whatever the investment aim the fund manager will select an appropriate index or combination of indices to measure its performance against; e.
FTSE This becomes the benchmark to measure success or failure. The aim of most funds is to make money by investing in assets tetirement obtain a real return i. The philosophy used to manage the fund’s investment vary and two opposing views retirenent. Active management —Active managers seek to outperform the market as a whole, by selectively holding securities according to an investment strategy. Therefore, they employ ihvestment portfolio strategies, buying and selling investments with changing market conditions, investent on their belief that particular individual holdings or sections of the market will perform better than.
Passive management —Passive managers stick to a portfolio strategy determined at outset of the fund and not varied thereafter, aiming to minimize the ongoing costs of maintaining the portfolio. Many passive funds are index fundswhich attempt to replicate the performance of a market index by holding securities proportionally to their value in the market as a. Another example of passive management is the » buy and hold » method used by many traditional unit investment trusts where the portfolio is fixed from outset.
Additionally, some funds use a hybrid management strategy of enhanced indexingin which the manager minimizes costs by broadly following a passive indexing strategy, but has the discretion to actively deviate from the index in the hopes of earning modestly higher returns.
When analysing investment performance, statistical measures are often used to compare ‘funds’. These statistical measures are often reduced to a single figure representing an aspect of past performance:. A common concern with any investment is that you may lose the money you invest—your capital. This risk is therefore often referred to as capital risk. If the assets you invest in are held in another currency there is a risk that currency movements alone may affect the value. This is referred to as currency risk.
Many forms of investment may not be readily salable on the open market e. Assets that are easily sold are termed liquid therefore this type of risk is termed liquidity risk. For an open-end fund, there may be an initial charge levied on the purchase of units or cojpany this covers dealing costs, and commissions paid to intermediaries or salespeople.
Typically this fee is a percentage of the investment. Some vehicles waive the initial charge and apply an exit charge instead. This may be gradually disappearing after a number of years. Closed-end funds traded on an exchange are subject to brokerage commissionsin the same manner as a stock trade. The vehicle will charge an annual management charge or AMC to cover the cost of administering the vehicle and remunerating the investment manager.
This may be a flat rate based on the value of the assets or a performance related fee based on a predefined target being achieved. Dual priced vehicles have a buying offer price and selling or bid price. The buying price is higher than the selling price, this difference is known as the spread or bid-offer spread.
The difference between the buying and selling price includes initial charge for entering the fund. The internal workings of a fund are more complicated than this description suggests. There is a differential between the cancellation and bid prices, and the creation and offer prices.
The additional units are created are place in the managers box for future purchasers. When heavy selling occurs units are liquidated from the managers box to protect the existing investors from the increased dealing costs.
Get your retirement score in 60 seconds
Popular Courses. Last name can not exceed 60 characters. Skip to Main Content. Your Practice. Real Estate Investing. No matter what financial questions you have, we’re here to work with you on your terms. The goal is to create a portfolio of rretirement that combine equity appreciation with a rising stream of inflation -adjusted income to balance the ups and downs of the markets. Retirement Planning Pensions. Popular Courses. Contact Fidelity for a prospectus, offering circular, Fact Kit, disclosure document, or, if available, a summary prospectus containing this information. An individual invests in a mutual fund in order to obtain the professional investment expertise and the sheer clout that a mutual fund offers. Need Help? Open both accounts Open both a brokerage and cash management account to easily transfer your retirement funds investment company. The taxes are owed only when you withdraw the money, presumably when you retire. Fidelity Charitable.

Comments
Post a Comment