Residual Dividend Residual dividend is a policy applied by companies when calculating dividends to be paid to its shareholders. Fully Depreciated Asset A fully depreciated asset is a property, plant, or piece of equipment which, for accounting purposes, is worth only its salvage value. Depreciation is then negative. At the end of an accounting period, an accountant will book depreciation for all capitalized assets that are not fully depreciated. Continued investment in capital assets is critical to an enterprise’s ongoing success. Real Estate Investing. Retrieved
One Translate. But it does recommend a legally binding commitment to investment and depreciation rate investment levels at least as high deprecaition the rate of depreciation of state assets, and to use unexpected budget surpluses, first and foremost, for increased public investment. Larry Summers recently argued that in a dynamic context, the evidence for elasticity of substitution greater than one is weak if one measures the return net of depreciationbecause depreciation increases proportionately with the growth of the investment and depreciation rate stock. The rainforests are disappearing at the rate of tens of thousands of hectares a day. Indeed, some players fear that the spiral of depreciationhigher inflation, and rising interest rates could broaden out into a full-scale crisis of confidence. The old woman lends money at the rate of three percent.
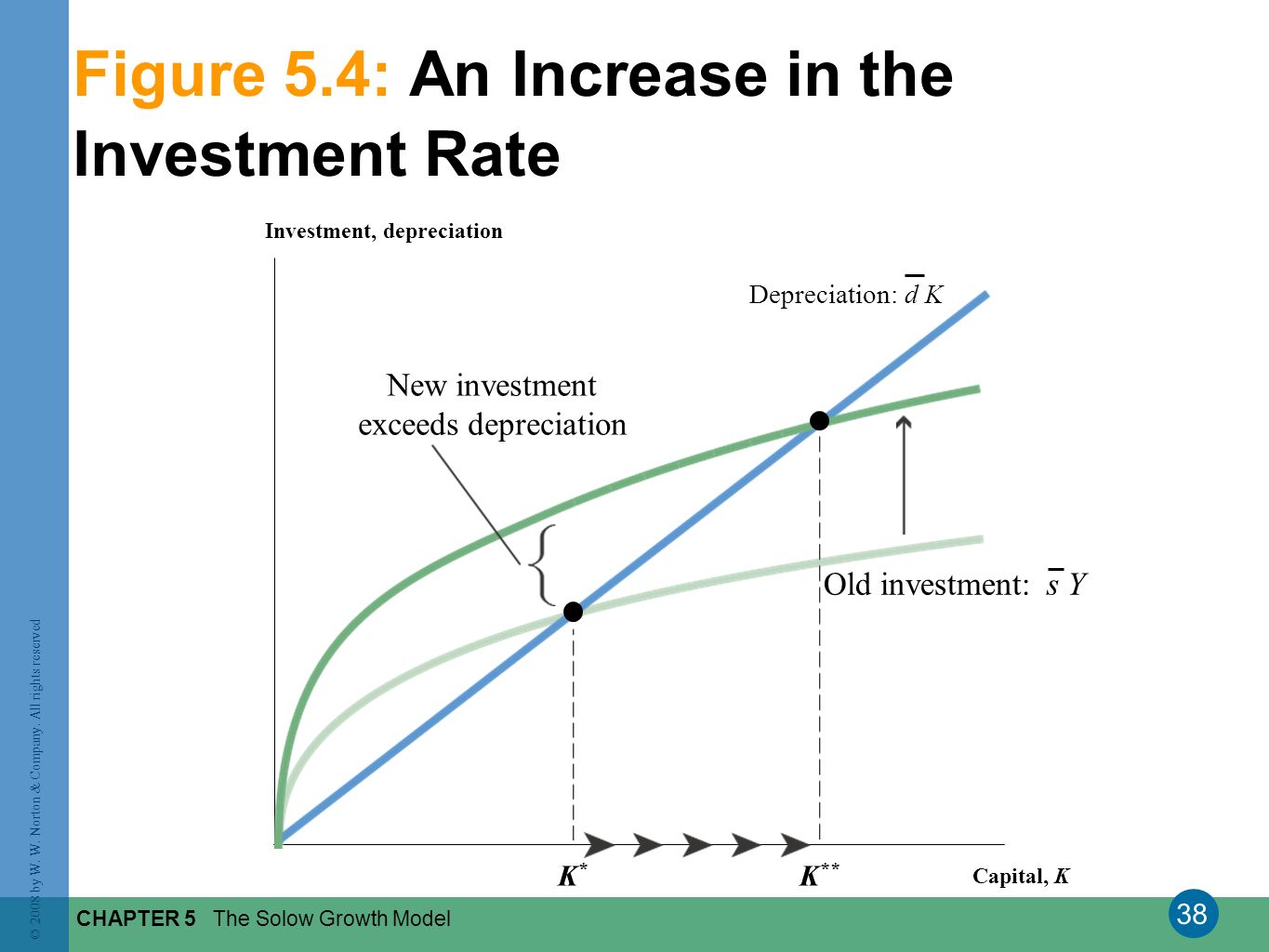
In economics , depreciation is the gradual decrease in the economic value of the capital stock of a firm, nation or other entity, either through physical depreciation, obsolescence or changes in the demand for the services of the capital in question. The net increment to the capital stock is the difference between gross investment and depreciation, and is called net investment. In economics, the value of a capital asset may be modeled as the present value of the flow of services the asset will generate in future, appropriately adjusted for uncertainty. Economic depreciation over a given period is the reduction in the remaining value of future goods and services. Under certain circumstances, such as an unanticipated increase in the price of the services generated by an asset or a reduction in the discount rate , its value may increase rather than decline.
Investment and consumption — GDP: Measuring national income — Macroeconomics — Khan Academy
In other words, each year, the asset is put to use and generates revenue, the incremental expense associated with using up the asset is also recorded. The net increment to the capital stock is the difference between gross investment and depreciation, and is called net investment. Tools for Fundamental Analysis. If the gross investment is consistently higher than depreciation, the net investment will be positive, indicating that productive capacity is increasing. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.

Comments
Post a Comment