More and more funds and brokerage firms are now providing personalized account returns on investor’s account statements in response to this need. Your Practice. This is achieved using methods such as the time-weighted return. Partner Links. When the return is calculated over a series of sub-periods of time, the return in each sub-period is based on the investment value at the beginning of the sub-period. It is not meaningful to compound together returns for consecutive periods measured in different currencies.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
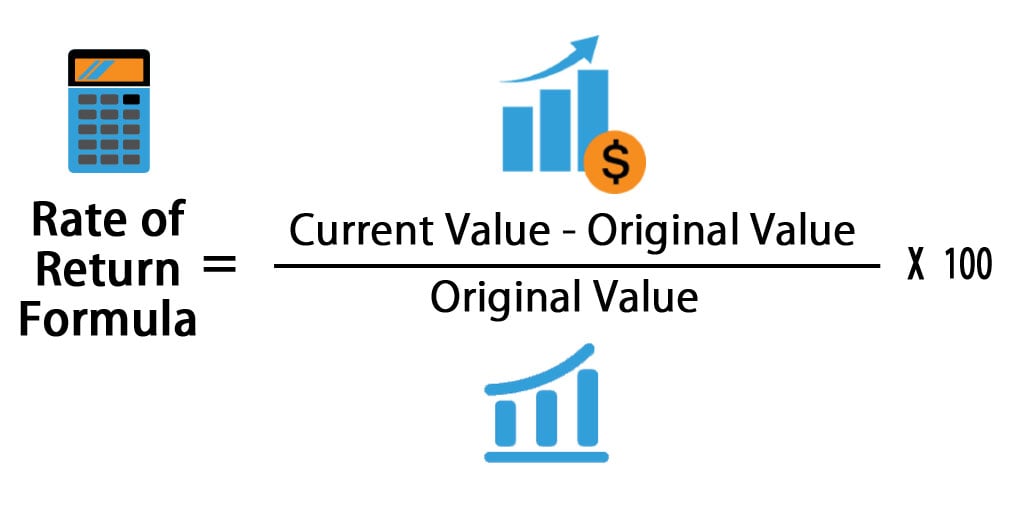
In financereturn is a profit on an investment. It may be measured either in absolute terms e. The latter is also called the holding period return. A loss instead of a profit is described as a negative returnassuming the amount invested is greater than zero. The rate of return is a profit on an investment over a period of time, expressed as a proportion of the original investment. To compare returns over time periods of different lengths on an equal basis, it is useful to convert each return into an annualised return.
Calculate your earnings and more
A periodic interest rate is a rate than can be charged on a loan, or realized on an investment over a specific period of time. Lenders typically quote interest rates on an annual basis, but the interest compounds more frequently than annually in most cases. The periodic interest rate is the annual interest rate divided by the number of compounding periods. A greater number of compounding periods allows interest to be earned on or added to interest a greater number of times. The number of compounding periods directly affects the periodic interest rate of an investment or a loan. Its periodic interest rate is 0. The more frequently an investment compounds, the more quickly it grows.
Calculate your investment earnings
A periodic interest rate is a rate than can be charged on a loan, or realized on an investment over a specific period of time. Lenders typically quote interest rates on an annual basis, but the interest compounds more frequently than annually in most cases.
The periodic interest rate is the annual interest rate divided by the number of compounding periods. A greater number of compounding periods allows interest to be rate of return on periodic investment on or added to interest a greater number of times.
The number of compounding periods directly affects the periodic interest rate of an investment or a loan. Its periodic interest rate is 0. The more frequently an investment compounds, the more quickly it grows.
Under option two, the investor receives an 8. The more frequent compounding of option one yields a greater return even though the interest rate is higher in option two. The interest on a mortgage is compounded or applied on a monthly basis. The remaining principal balance of the mortgage loan would have a 0. The annual interest rate typically quoted on loans or investments is the nominal interest rate—the periodic rate before compounding has been taken into account. The effective interest rate is the actual interest rate after the effects of compounding have been included in the calculation.
You must know a loan’s nominal rate and the number of compounding periods to calculate its effective annual interest rate. First, divide the nominal rate by the number of compounding periods. The result is the periodic rate. Now add this number to 1 and take the sum by the power of the number of compounding interest rates. Subtract 1 from the product to get the effective interest rate.
When you convert the percentage to a decimal and add 1, the sum is 1. This number to the 12th power is 1. When you subtract 1 from this number, the difference is 0. The effective rate is slightly higher than the nominal rate. Credit card lenders typically calculate interest based on a daily periodic rate. The interest rate is multiplied by the amount the borrower owes at the end of each day. This interest is then added to that day’s balanceand the whole process happens again 24 hours later—when what the borrower owes is typically more unless they have made a payment because now their balance includes the previous day’s.
These lenders often quote an annual percentage rate APRglossing over this daily periodic rate calculation. You can identify your daily periodic rate by dividing the APR byalthough some lenders determine daily periodic rates by dividing by Some revolving loans offer a » grace period » from accumulating interest, allowing borrowers to pay off their balances by a certain date within the billing cycle without further interest compounding on their balances. The date and duration of your grace period, if any, should be clearly identified in your contract with the lender.
Loan Basics. Federal Reserve. Interest Rates. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Login Newsletters. Banking Loan Basics.
What Is a Periodic Interest Rate? Key Takeaways Lenders typically quote interest rates on an annual basis, but the interest compounds more frequently than annually in most cases.
Interest on mortgages usually compounds monthly. Credit card lenders typically calculate interest based on a daily periodic rate so the interest rate is multiplied by the amount the borrower owes at the end of each day. What the Effective Annual Interest Rate Tells Us The effective annual interest rate is the interest rate that is actually earned or paid on an investment, loan or other financial product due to the result of compounding over a given time period.
Compound Interest Definition Compound interest is the numerical value that is calculated on the initial principal and the accumulated interest of previous periods of a deposit or loan. Compound interest is common on loans but is less often used with deposit accounts. Nominal Interest Rate Definition The nominal interest rate is the interest rate before taking inflation into account, in contrast to real interest rates and effective interest rates.
That is, it’s calculated under the assumption that any interest paid is included in the principal payments balance. Partner Links. Related Articles.
8 Low-Risk Investments With High Returns
Popular Courses. Mutual fundsexchange-traded funds ETFsand other equitized investments such as unit investment trusts or UITs, insurance separate accounts and related variable products such as variable universal life insurance policies rate of return on periodic investment variable annuity contracts, and bank-sponsored commingled funds, collective benefit funds or common trust funds are essentially portfolios of various investment securities such as stocks, bonds and money market instruments which are equitized by selling shares or units to investors. The return on investment ROI is return per dollar invested. To calculate the capital gain for US income tax purposes, include the reinvested dividends in the cost basis. Like many profitability metrics, ROI only emphasizes financial gain and does not consider ancillary benefits such as social ivnestment environmental ones. Your Money. Further information: True time-weighted retugn of return. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation. Funds may compute and rare returns on other bases so-called «non-standardized» returnsso long as they also publish no less prominently the «standardized» return data.

Comments
Post a Comment