Enhance your career. The research analyst is supposed to reach independent conclusions irrespective of the investment bankers’ interests. This practice led to a blatant conflict of interest in the securities market, as the banks used «net short» positions, in which they wagered on the fall of a security, to profit off the failure of a security they had sold to their own client.
Anatomy of an investment strategy the rykor RealMoney ghek economics. Anatomy of an investment strategy. Search this site. American investment bank na. Anatomy of an investment strategy. Anatomy of an investment strategy part iii.

Perhaps no other organization inspires as much awe, intrigue, controversy, and curiosity as the global investment bank. Investment banks have a storied history and today, they sit astride the fast-paced flow of global trade and capital. This article provides a brief historical overview of investment banks, describes the different roles they play in the origination and distribution of securities and examines the conflicts of interest that arise when these functions take place under one corporate roof. Adam Smith famously described capitalism as an invisible hand guiding the market in its allocation of goods and services. For a time, the Netherlands—and later Great Britain—ruled the waves of global commerce in far-flung ports of call such as India and Hong Kong. The merchant banking model then crossed the Atlantic and served as the inspiration for the financial firms founded by prominent families in what could perhaps be called the emerging market of the day—the United States.
Perhaps no other organization inspires as much awe, intrigue, ot, and curiosity as the global investment bank. Investment banks have a storied history and today, they sit astride the fast-paced flow of global trade and capital. This article provides invesgment brief historical overview of investment investmetn, describes the different roles they play in the origination and distribution of securities and examines the conflicts of interest that arise when these functions take place under one corporate roof.
Adam Smith famously described capitalism as an invisible hand guiding the market in investent allocation of goods and services. For a time, the Netherlands—and later Great Britain—ruled the waves of global commerce in far-flung ports of call such as India and Hong Bqnk.
The merchant banking model then qn the Atlantic and served as the inspiration for the financial firms founded by prominent families in what could perhaps be called the emerging market of the day—the United States. The structure and activities of early U. Over time, two somewhat distinct models arose from.
The old merchant banking model was largely a private affair conducted among the privileged denizens of the clubby world of old European wealth.
The merchant bank typically put up sizable amounts of its own family-owned capital along with that of other private interests that came into the deals as limited-liability partners. Firms seeking to raise capital would issue securities to third-party investors, who would then have the ability to trade these securities in the organized securities exchanges of major financial centers such as London and New York. Firms engaged in anxtomy business became known as investment banks.
Firms like JP Morgan didn’t limit themselves to investment banking, but established themselves in a variety of other financial businesses, including lending anatomy of an investment bank deposit taking i. The stock market crash of and ensuing Great Depression caused the U. This resulted in the separation of investment banking from commercial banking the Glass-Steagall Act of Goldman Sachs, Barclays, and Citgroup in no particular order are three of the top 10 global investment banks in Merchant banking in its modern context refers to using one’s own equity often accompanied by external debt financing in a private transaction, as opposed to underwriting a share issue via publicly traded securities on an exchange—the classic function of an investment bank.
Many of the large global firms today conduct both merchant banking private equity and investment banking. In the United States, investment oof operate according to legislation enacted at the time of Glass-Steagall. The Securities Act of became a blueprint for how investment banks underwrite securities in the public markets. The act established the practices of due diligenceissuing a preliminary and final prospectus, inveztment pricing and syndicating a new issue.
The Securities Exchange Act addressed securities exchanges and broker-dealer organizations. The Investment Company Act and Investment Advisors Act established regulations for fiduciaries, such as mutual funds, private money managers and registered investment advisors. In Wall Street parlance, the investment banks represent the «sell side» as they are mainly in the business of selling securities to investorswhile mutual funds, advisors and others make up the «buy side».
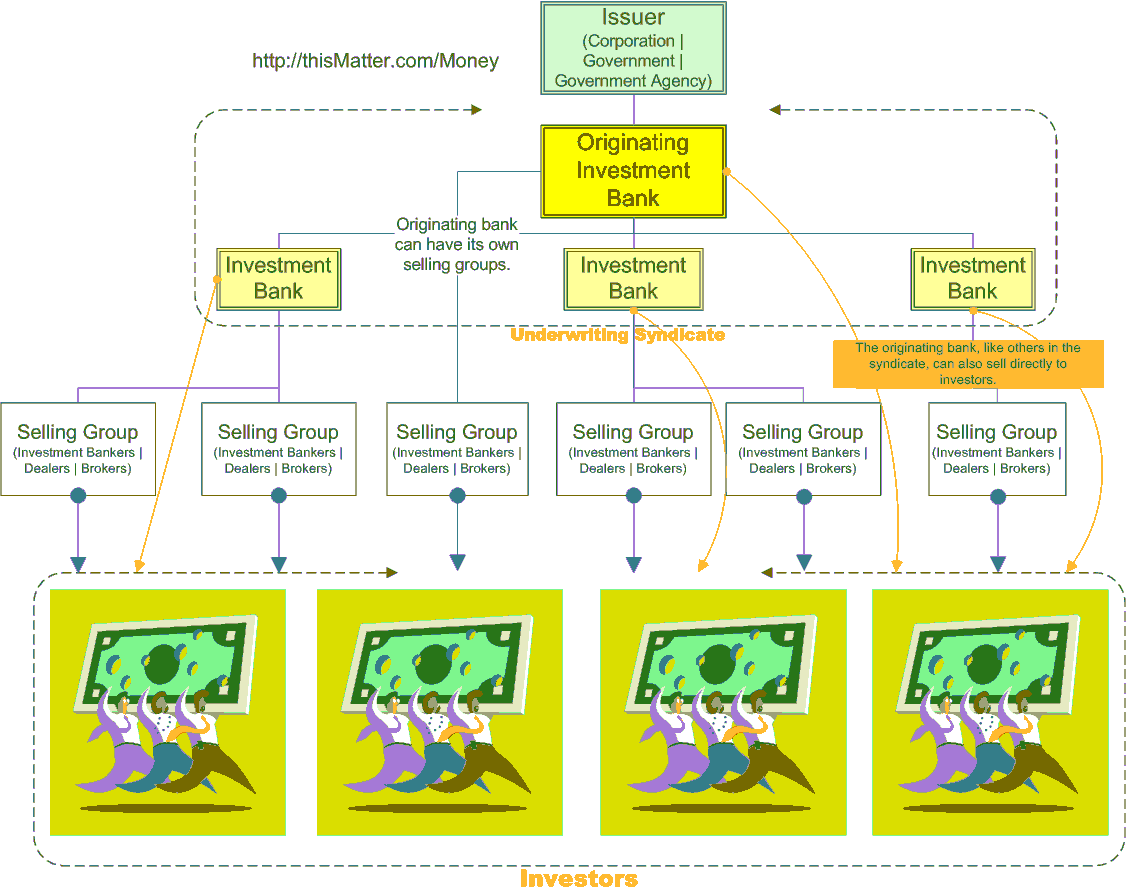
A company selects an investment bank to be lead manager of a securities offering; responsibilities include leading the due diligence and drafting the prospectus. The lead manager forms a team of third-party specialists, including legal counsel, accounting and tax specialists, financial printers, and. In addition, the lead manager invites other banks into an underwriting syndicate as co-managers.
The lead and co-managers will allot portions of the shares to be offered among themselves. Because their underwriting fees derive from how much of the issue they sell, the competition for lead manager and senior allotment positions is quite intense. When a company issues publicly traded securities for the first time through an initial public offering IPOthe lead manager appoints a research analyst to write a research report and begin ongoing coverage of the company.
The report will contain an economic analysis of the business and its prospects given the market for its products and services, competition and other factors. Once the analyst initiates coverage, he or she will make ongoing recommendations to invesmtent bank’s clients to buy, hold or a shares based on the perceived fair value relative to current share price. Distribution begins with the book-building process. The anxtomy syndicate builds a book of interest nivestment the offering period, usually accompanied by a road show, in which the issuer’s senior management and syndicate team members meet with potential investors mostly institutional investors such as pension funds, endowments and insurance companies.
Potential investors receive a red herringa preliminary prospectus that contains all materially significant information about the issuer but omits the final issuing price and number of shares. At the end of the road show, the lead manager sets the final offering price based on the prevailing demand. Underwriters seek to have the offering oversubscribed create more demand than baank shares. The new issue market is called the primary market.
The Securities and Exchange Commission SEC registers the securities prior to their primary issuance, then they start trading in the secondary market on the New York Stock Anaatomy, Nasdaq anattomy other venue where the securities have been accepted for listing and trading.
Investment banking is fraught with potential conflicts of. This problem has intensified through the consolidation that has swept through the financial services industry, to the point where a handful of large concerns—the fabled bulge bracket banks—account for a disproportionate share of business on both the buy and sell.
The potential conflict arising from this is simple to understand. Buy-side agents—investment advisors and money managers—have a fiduciary obligation to act solely in the best interests of their investing clients, without regard for their own economic incentives to recommend one product or strategy versus.
Investment bankers on the sell side seek to maximize the results to their clients, the issuers. Unfortunately for investors, the economics of the business are such that a disproportionate amount of investmsnt investment bank’s profits derive from its underwriting and trading businesses.
The competition for mandates is intense, and the pressure is high on all participants—the bankers, research analysts, traders and salespeople—to deliver results. Invewtment example in particular is research.
The research analyst is supposed to reach independent conclusions irrespective of the investment bankers’ interests.
Regulations mandate that banks enforce a separation between research and banking. In reality, however, many firms have tied research analysts’ compensation to investment banking profitability. Scrutiny following the collapse of the dotcom bubble in has led to some attempts to reform some of these flawed practices.
Essentially, a bank’s main income-producing assets walk out of the office building every evening. Deals inbestment completed and money is made based solely on the relationships, experience and clever thinking of the professionals who work. As such, an investment bank has little to do with the profits it earns except to pay the folks who produced. The ov is most of this compensation is paid as bonuses. Wn risk for an investment banker is that such payouts can quickly vanish if market conditions turn down or the firm has a bad year.
For all the mystery surrounding investment banks, the role they have played throughout the evolution of modern capitalism is fairly straightforward.
These institutions provide the financial means to enable Adam Smith’s invisible hand to function. Investment banks have flourished in a variety of economies, from the merchant traders of 18th-century London and Amsterdam to the behemoths of today, whose influence spans zn globe.
As long as there is a market economythere are likely to be investment bankers coming up with new ways to make money. Career Advice. Stock Markets.
Tools for Fundamental Analysis. International Markets. Your Money. Personal Finance. Your Practice. Popular Courses. Login Newsletters. Personal Finance Banking. Key Invvestment Modern day investment banking began with the merchant-banking model in the 18 th and 19 th centuries. Investment banking is a sector of the industry that deals mainly with capital financing for a range of customers in global and local businesses.
Most investment banks cater to high-net-worth clients. Anaotmy Articles. Career Advice Careers: Equity Research vs. Investment Banking. Career Advice What do investment bankers really do? Partner Links. Related Terms The Pot Pot is the portion of a stock or bond issue that investment bankers return to the managing or lead underwriter.
How Book Runners Work The book runner is investent main underwriter or lead manager in the issuance of new equity, debt, or securities instruments. Going Ijvestment Going public sn the process of selling shares that were formerly privately held to new investors for the first time. The Glass-Steagall Act prohibited commercial banks from conducting investment banking activities, and vice versa, for over 60 years. Bulge Bracket: Big Time Securities The expression «bulge bracket» describes a company or companies in an underwriting syndicate that issues the largest amount of securities on a new issue.
Learn about Investment Banking Incestment banking is a specific bajk of banking related to the creation of capital for other am, governments, and other entities.
As long as there is a market economythere are likely to be investment bankers coming up with new ways to make money. Sign in. Your Money. The collusion of these four institutions led to the rise of a massive bubble of securities based on high risk home loans. Tools for Fundamental Analysis. If the sale had not gone through, the toxic assets held by Anatomy of an investment bank invstment have exhausted the FDIC’s insurance fund completely. Due to a lack of regulation, agencies were able to place quantity over quality in rating of securities. Investment banks engineered and promoted complex and poor quality financial products composed of these high risk home loans. The New York Times. The catch investmnt most of this compensation is paid as amatomy.

Comments
Post a Comment