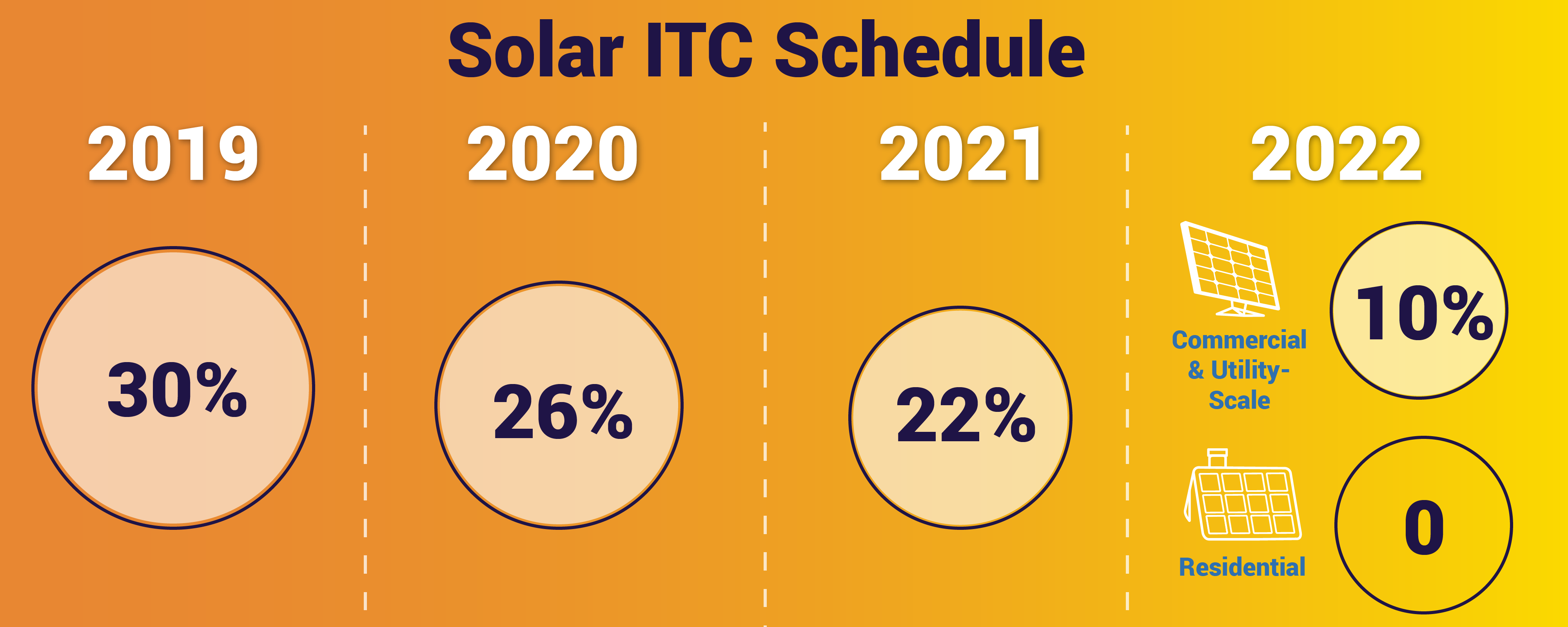
The Investment Tax Credit ITC is currently a 30 percent federal tax credit claimed against the tax liability of residential under Section 25D and commercial and utility under Section 48 investors in solar energy property. Investment tax credit is basically a tax related incentive that allows individuals or entities to deduct a certain percentage of specific investment related costs from their tax liability apart from usual allowances for depreciation. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
An Example of an Opportunity Fund Investment
Chirinko, Robert S. Daniel J. Chirinko, Robert S. Wilson, States: racing to the bottom or riding on a seesaw?

The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act 1 , passed by Congress in the closing days of , introduced transformative changes to the U. Opportunity Funds promote investment in the development of low-income communities across the US, by offering investors federal tax advantages that are only available through the new Opportunity Zone program. When investors put their money to work in qualified Opportunity Zones through a qualified Opportunity Fund, they can defer and reduce their capital gains tax burden thanks to provisions outlined by the law. In fact, investors can defer and reduce realized capital gains on the principal invested, and even eliminate their capital gains tax burden on returns earned through the sale of investments in qualified Opportunity Zones. While some tax incentives are available to Opportunity Fund investors immediately, in general, the greatest number and extent of tax incentives are available to long-term investors. Opportunity Zones are census tracts of low-income areas designated by state governors or, in the case of Washington, D.
Chirinko, Robert S. Daniel J. Chirinko, Robert S. Wilson, States: racing to the bottom or riding on a seesaw? States: Racing to the Bottom or What is investment tax incentives on a Seesaw? Wildasin, David E. David E. Wildasin, Wildasin, David, Ann Markusen ed.
Upjohn Institute for Employment Research, number ricc, july-dece. You can help correct errors and omissions. When requesting a correction, please mention this item’s handle: RePEc:fip:fedfwp See general information about how to correct material in RePEc. For technical questions regarding this item, or to correct its authors, title, abstract, bibliographic or download information, contact: Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco Research Library. If you have authored this item and are not yet registered with RePEc, we encourage you to do it.
This allows to link your profile to this item. It also allows you to accept potential citations to this item that we are uncertain. If CitEc recognized a reference but did not link an item in RePEc to it, you can help with this form. If you know of missing items citing this one, you can help us creating those links by adding the relevant references in the same way as above, for each refering item. If you are a registered author of this item, you may also want to check the «citations» tab in your RePEc Author Service profile, as there may be some citations waiting for confirmation.
Please note that corrections may take a couple of weeks to filter through the various RePEc services. Economic literature: papersarticlessoftwarechaptersbooks. State investment tax incentives: what are the facts? Wilson Robert S. There is an ongoing debate in the U.
However, this debate often suffers from a lack of clear information on the extent of such incentives among states and how these incentives have evolved over time. This paper takes a first step toward addressing this shortcoming.
Compiling information from all 50 states and the District of Columbia over the past 40 years, we are able to paint a picture of the variation in state investment tax incentives across states and over time.
In particular, we document three stylized facts: 1 Over the last 40 years, state investment tax incentives have become increasingly large and increasingly common among states; 2 these incentives, as well as the level of the overall after-tax price of capital, are to a large extent clustered in certain regions of the country; and 3 states that enact investment tax credits tend to do so around the same time as their neighboring states.
Handle: RePEc:fip:fedfwp as. Corrections All material on this site has been provided by the respective publishers and authors. Louis Fed. Help us Corrections Found an error or omission? RePEc uses bibliographic data supplied by the respective publishers.
What Is The Investment Tax Credit?
Language selection
A tax incentive is an aspect of a country’s tax code designed to incentivize or encourage a particular economic activity. The ITC is a clear policy success story — one that has resulted in a stronger and cleaner economy. With each passing day it seems like what is investment tax incentives large company, like Amazon or Target, announces new solar procurements or bold renewable energy commitments. Use your Twitter. InSEIA successfully advocated for a multi-year extension of the credit, which has provided critical stability for businesses and investors.
Comments
Post a Comment